Disentangling Multi-Scale Anomaly Signals in Networks via Scale-Aware Contrastive Learning
Arriola, M., Kosan, M., Huang, Z., Sharma, S., Singh, A.
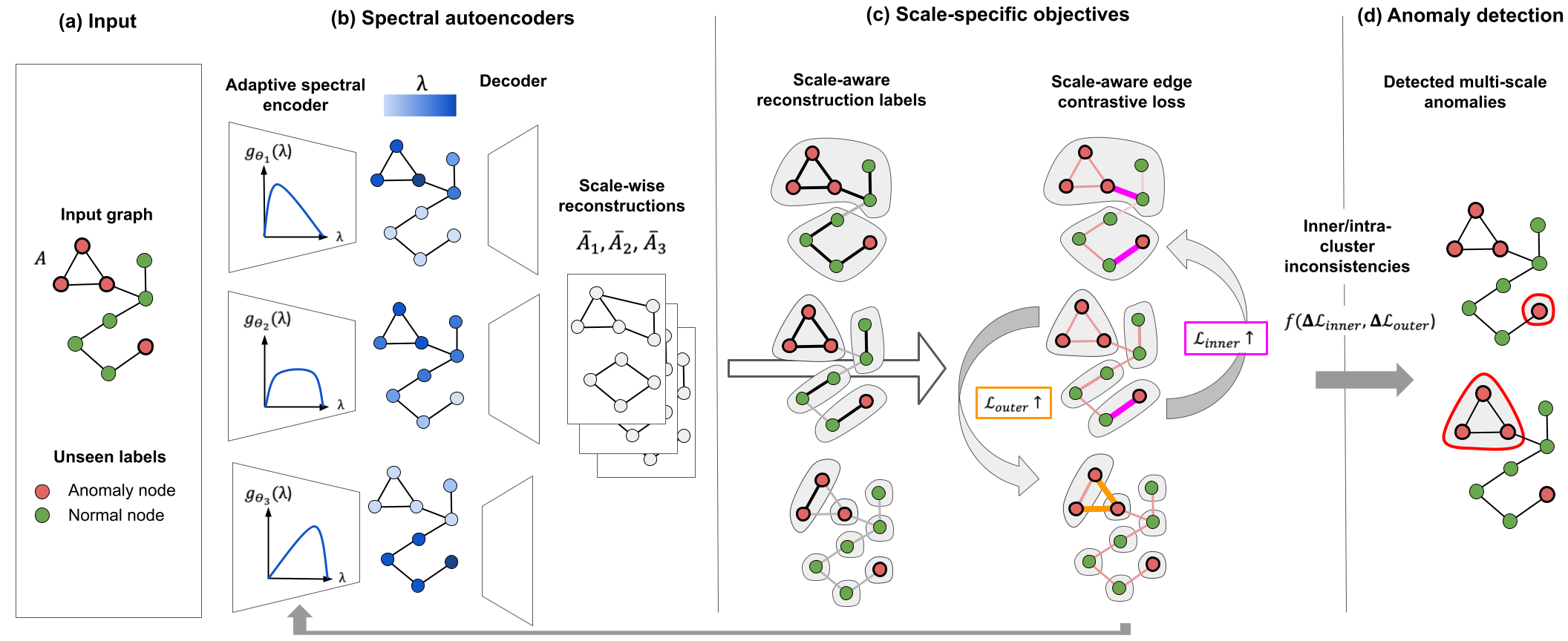
Detecting suspicious or unexpected patterns in networks without supervision is challenging because it requires heuristic knowledge about anomaly characteristics which is often unavailable in real-world settings. We perform extensive analysis on newly introduced real-world data with labelled ground-truth anomalies and identify cohesive anomalous communities that operate multiple scales based on their spatial and spectral profiles. We address multi-scale anomalous subgraph detection by introducing Multi-Scale Graph Anomaly Detection (MuSGAD), a self-supervised framework that learns multi-scale node embeddings via a multi-scale spectral filters and a contrastive learning objective, then flags anomalies with high residuals.
